What is n-type and P-type?
Doping of semiconductors Pentavalent impurities Impurity atoms with 5 valence electrons produce n-type semiconductors by contributing extra electrons. Trivalent Impurities Impurity atoms with 3 valence electrons produce p-type semiconductors by producing a “hole” or electron deficiency.
How n-type and p-type are formed?
A p-type semiconductor is formed when group III elements are doped into a complete semiconductor material. In contrast, an n-type semiconductor is created when group V elements are doped into an intrinsic semiconductor.
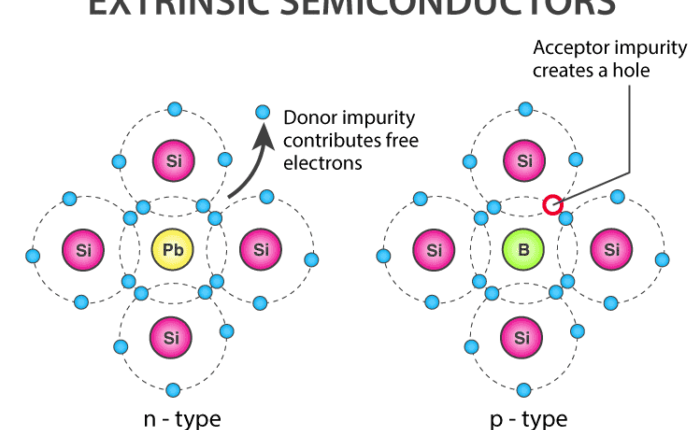
How is P-type produced? The extrinsic p-type semiconductor is formed when a trivalent impurity is added to a pure semiconductor in a small amount, and as a result, a large number of holes are formed in it. A large number of holes are provided in the semiconductor material by the addition of trivalent impurities such as gallium and indium.
How are p and n-type materials created?
A PN junction is formed when an n- and p-type material are fused together to make a semiconductor diode. It all comes down to the p-n junction. N-type silicon has extra electrons and there are atoms on the p-side that need electrons, so electrons travel across the junction.
How n-type and p-type semiconductors are obtained?
Semiconductors of n-type and p-type can be obtained by doping pure silicon or germanium with pentavalent elements such as P, As and trivalent elements such as Al, In, respectively.
How do you make n-type and p-type?
Doping of semiconductors Pentavalent impurities Impurity atoms with 5 valence electrons produce n-type semiconductors by contributing extra electrons. Trivalent Impurities Impurity atoms with 3 valence electrons produce p-type semiconductors by producing a “hole” or electron deficiency.
How do you make n-type and p-type semiconductors?
Doping of semiconductors Pentavalent impurities Impurity atoms with 5 valence electrons produce n-type semiconductors by contributing extra electrons. Trivalent Impurities Impurity atoms with 3 valence electrons produce p-type semiconductors by producing a “hole” or electron deficiency.
How semiconductors of both p-type and n-type are produced?
Pentavalent impurities Impurity atoms with 5 valence electrons produce nâtype semiconductors by contributing extra electrons. Trivalent Impurities Impurity atoms with 3 valence electrons produce pâ-type semiconductors by producing a “hole” or electron deficiency.
How are N-type semiconductors made?
An n-type semiconductor is the result of implantation of doping atoms that have more electrons in their outer (bonding) shell than silicon. The resulting semiconductor crystal contains excess, or free, electrons that are available to conduct current.
How is N-type formed?
An n-type semiconductor is the result of implantation of doping atoms that have more electrons in their outer (bonding) shell than silicon. The resulting semiconductor crystal contains excess, or free, electrons that are available to conduct current.
How is N-type semiconductor prepared?
When pentavalent impurities (As, Sb) atoms are introduced into pure semiconductor, it becomes an electron-rich conductor which makes them negatively charged. They are attracted towards positively charged leader. Results in N-type semiconductor.
How is an N-type material created?
An N-type semiconductor is a type of material used in electronics. It is made by adding an impurity to a pure semiconductor such as silicon or germanium. The impurities used may be phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, bismuth or another chemical element. They are called donor impurities.
What is n-type in chemistry?
An N-type semiconductor is a type of material used in electronics. It is made by adding an impurity to a pure semiconductor such as silicon or germanium. The impurities used may be phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, bismuth or another chemical element. They are called donor impurities.
What are the examples of n-type? Examples of N-type semiconductor Examples of N-type semiconductors are silicon doped with arsenic, silicon doped with phosphorus, arsenic doped with Germanium, Germanium doped with phosphorus, and so on are n-type semiconductor examples.
What is n-type material example?
N-type semiconductor examples are Sb, P, Bi and As. These materials include five electrons in their outer shells. The four electrons will make covalent bonds using the adjacent atoms, and the fifth electron will be available as a current carrier. So that impurity atom is called a donor atom.
What is n-type and p-type material?
Most carriers in a p-type semiconductor are holes. In an n-type semiconductor, pentavalent impurity from the V group is added to the pure semiconductor. Examples of pentavalent impurities are arsenic, antimony, bismuth etc. The pentavalent impurities provide extra electrons and are referred to as donor atoms.
What are n-type materials?
An n-type semiconductor is an intrinsic semiconductor doped with phosphorus (P), arsenic (As) or antimony (Sb) as an impurity. Silicon in group IV has four valence electrons and phosphorus in group V has five valence electrons.
What is difference between n-type and p-type?
The basic difference between P-type and N-type semiconductors is that in an n-type semiconductor there is an excess of negatively charged carriers. In a p-type semiconductor, there is an excess of positively charged carriers (holes, which can be thought of as the absence of an electron).
Which is best n-type or p-type?
Impurities based on the number of valence electrons can be n-type (5) or p-type (3). n-type tendencies are a better choice due to reducing LID (Light Induced Degradation) and increasing durability and performance compared to p-type.
What is the difference between N and P-type of semiconductors draw diagrams to explain them?
In the n-type semiconductor, electrons are the majority carriers, and holes are the minority carriers. The electron density is much greater than the hole density in the n-type semiconductor denoted as ne >> nh, while in the p-type semiconductor the hole density is much greater than the electron density nh >> ne.
What is meant by n-type?
N-type definition ÄntÄ«s. Made of material, usually a semiconductor such as silicon, that is doped with impurities so that it has an excess of conduction electrons. 3. Made of material, usually a semiconductor such as silicon, that is doped with impurities so that it has an excess of conduction electrons.
Why is it called n-type?
As a main difference, in n-type semiconductors, the electrons have a negative charge, hence the name n-type.
What is n-type and p-type?
| N-type semiconductor | P-type semiconductor |
|---|---|
| In an N-type semiconductor, the majority of charge carriers are free electrons, while holes are in the minority. | In a P-type semiconductor, the majority of charge carriers are holes, while the free electrons are in the minority. |
What is meant by p-type material?
What is P-type material? Semiconductors such as germanium or silicon doped with any of the trivalent atoms such as boron, indium or gallium are called p-type semiconductors. The impurity atom is surrounded by four silicon atoms. It allows the atoms to fill only three covalent bonds, as it has only three valence electrons.
How p-type material is shape? These materials are formed by the deliberate addition of impurities to pure semiconductor materials, such as silicon. p-type semiconductors contain holes, mobile vacancies in the electronic structure that simulate positively charged particles, while n-type semiconductors contain free electrons.
Why is it called p-type semiconductor?
An extrinsic semiconductor doped with electron acceptor atoms is called a p-type semiconductor, because the majority of charge carriers in the crystal are positive holes.
What are holes in p-type semiconductor?
hole. P-type (for excess positive charges) silicon occurs if the dopant is boron, which contains one less electron than a silicon atom. Each added boron atom creates a deficiency of one electron – that is, a positive hole.
What is n-type and p-type semiconductor?
Most carriers in a p-type semiconductor are holes. In an n-type semiconductor, pentavalent impurity from the V group is added to the pure semiconductor. Examples of pentavalent impurities are arsenic, antimony, bismuth etc. The pentavalent impurities provide extra electrons and are referred to as donor atoms.
What is meant by p-type?
p-type in British English adjective. 1. (of a semiconductor) having a density of mobile holes that exceeds the density of conduction electrons. 2. relating to or resulting from the movement of holes in a semiconductor.
What is P-type silicon?
[â²pÄ ¦tÄ«p â²sil·Éâkän] (electronics) Silicon to which more impurity atoms of the acceptor type (with a valence of 3, such as boron) than of the donor type (with a valence of 5, such as phosphorus) have been added, with the result that the hole density exceeds the conduction electron density.
Is Phosphorus n type or p-type?
Phosphorus is an n-type dopant. It diffuses quickly, so it is usually used for bulk doping or for well formation. Used in solar cells.
What is p-type material In electronics?
What is a p-type semiconductor? A p-type semiconductor is an intrinsic semiconductor doped with boron (B) or indium (In). Silicon in group IV has four valence electrons and boron in group III has three valence electrons.
What is p-type material and n-type material?
p-type and n-type materials are simply semiconductors, such as silicon (Si) or germanium (Ge), with atomic impurities; the type of impurity present determines the type of semiconductor.
What are n-type and p-type semiconductors?
In an N-type semiconductor, the majority of charge carriers are free electrons, while holes are in the minority. In a P-type semiconductor, the majority of charge carriers are holes, while the free electrons are in the minority.
What is n-type and p-type?
| N-type semiconductor | P-type semiconductor |
|---|---|
| In an N-type semiconductor, the majority of charge carriers are free electrons, while holes are in the minority. | In a P-type semiconductor, the majority of charge carriers are holes, while the free electrons are in the minority. |
What are N- and P-type material? p-type and n-type materials are simply semiconductors, such as silicon (Si) or germanium (Ge), with atomic impurities; the type of impurity present determines the type of semiconductor.
What do mean by n-type and p-type semiconductors?
3. P-type semiconductors are positive type semiconductors, it means that a deficiency of 1 electron is required. N-type semiconductor is negative type semiconductor, it means that an excess of 1 electron is required. 4. In P-type semiconductors, the majority charge carriers are holes and the minority charge carriers are electrons.
What is meant by n-type semiconductor?
What is an n-type semiconductor? An n-type semiconductor is an intrinsic semiconductor doped with phosphorus (P), arsenic (As) or antimony (Sb) as an impurity. Silicon in group IV has four valence electrons and phosphorus in group V has five valence electrons.
What are n-type and p-type semiconductors give their applications?
Diode is a combination of n-type and p-type semiconductors widely used as rectifiers. Transistors are produced by sandwiching a layer of one type of semiconductor between two layers of another type of semiconductor. npn and pnp transistors are used to detect or amplify radio or audio signals.
What is P-type?
A p-type semiconductor is an extrinsic type of semiconductor. When a trivalent impurity (such as boron, aluminum, etc.) is added to an intrinsic or pure semiconductor (silicon or germanium), it is said to be a p-type semiconductor. Trivalent impurities such as boron (B), gallium (Ga), indium (In), aluminum (Al), etc.
What is meant by n-type?
N-type definition ÄntÄ«s. Made of material, usually a semiconductor such as silicon, that is doped with impurities so that it has an excess of conduction electrons. 3. Made of material, usually a semiconductor such as silicon, that is doped with impurities so that it has an excess of conduction electrons.
What is meant by n-type of semiconductor?
What is an n-type semiconductor? An n-type semiconductor is an intrinsic semiconductor doped with phosphorus (P), arsenic (As) or antimony (Sb) as an impurity. Silicon in group IV has four valence electrons and phosphorus in group V has five valence electrons.
Why is it called n-type?
As a main difference, in n-type semiconductors, the electrons have a negative charge, hence the name n-type.
Sources :


Comments are closed.